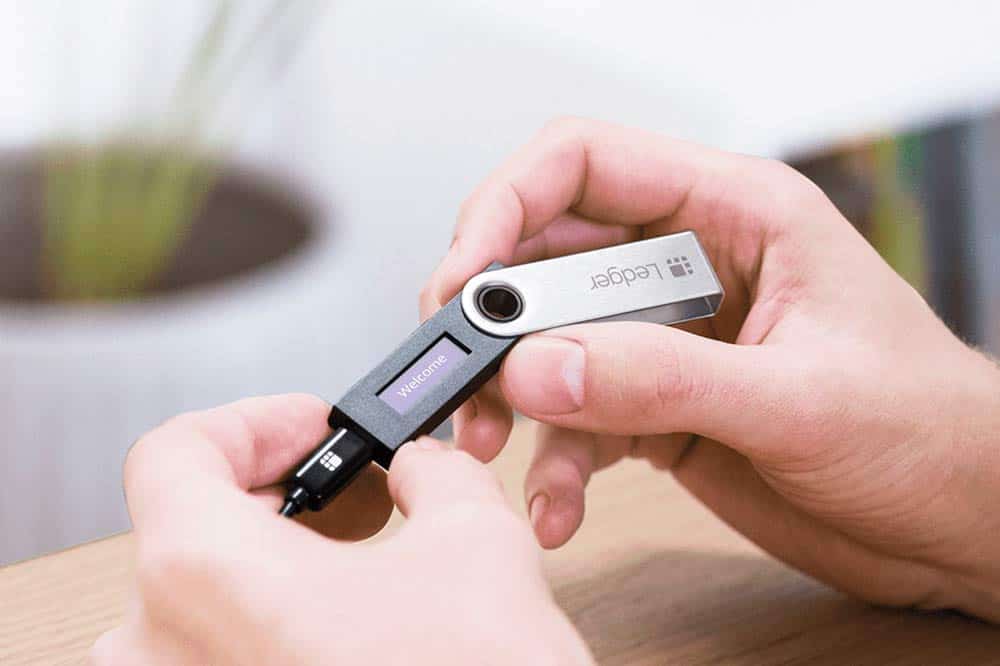
After identifying a malicious version of the Ledger Connect Kit, hardware wallet manufacturer Ledger advised users against connecting to decentralized applications (dapps). On December 14, a compromise occurred in the front ends of several decentralized applications (DApps) that utilized Ledger’s connector. These DApps comprised Zapper, SushiSwap, Phantom, Balancer, and Revoke.cash. After approximately three hours passed since the security vulnerability was identified, Ledger disclosed at 1:35 pm UTC that the authentic file had been substituted for the malignant one.
In addition to cautioning users “to always Clear Sign” transactions, Ledger asserts that only the addresses and data displayed on the Ledger interface are authentic. “Immediately halt the transaction if the screen displayed on your Ledger device differs from the screen on your computer or mobile device.”
Ledger confirmed the code vulnerability and declared that “a malicious version of the Ledger Connect Kit has been removed.” The company further stated that “a legitimate version is currently being pushed to replace the malicious file.”
🚨We have identified and removed a malicious version of the Ledger Connect Kit. 🚨
— Ledger (@Ledger) December 14, 2023
A genuine version is being pushed to replace the malicious file now. Do not interact with any dApps for the moment. We will keep you informed as the situation evolves.
Your Ledger device and…
Developers were the first to identify the compromised version of the Connect Kit, a library that facilitates the connection between the Ledger hardware wallet and decentralized applications (dapps), via a tweet. The Web3 security firm BlockAid stated, “The attacker injected a wallet draining payload” into the NPM package of the ledger connect kit. Additionally, the report stated that decentralized applications (dapps) that utilized Ledger’s connect-kit versions 1.1.4 and later were impacted, including Hey.xyz and Sushi.com.
Matthew Lilley, chief technical officer of SushiSwap, was one of the initial individuals to disclose the concern, highlighting the compromise of a widely utilized Web3 connector that enabled the injection of malignant code into multiple DApps. The Ledger library validated the compromise where the vulnerable code inserted the drainer account address, according to the on-chain analyst. Lilley attributed the ongoing compromise and vulnerability of multiple DApps to Ledger. According to the executive, Ledger’s content delivery network was compromised, and JavaScript was imported from that network.
🚨🚨🚨 RED ALERT 🚨🚨🚨:
— I'm Software 🦇🔊 (@MatthewLilley) December 14, 2023
Do not interact with ANY dApps until further notice. It appears that a commonly used web3 connector has been compromised which allows for injection of malicious code affecting numerous dApps.
The Ledger connector is a Ledger-maintained library utilized by numerous DApps. Due to the addition of a wallet drainer, asset depletion from a user’s account may not occur automatically. However, browser wallet prompts such as MetaMask will be displayed, which may grant access to the assets to malicious actors.
In recent months, Ledger has been subject to security concerns, particularly concerning the voluntary ID-based Recover service that has infuriated cryptocurrency users. A fraudulent Ledger app available on the Microsoft App Store defrauded unwitting customers of nearly $1 million in November. Subsequently, the company encountered censure in 2020 subsequent to a breach of its customer email database, which compromised the email addresses of over one million users.
Ledger published an analysis on X five hours subsequent to the breach. A phishing attack enabled an adversary to insert malicious code into Ledger’s Connect Kit, as confirmed by the revelation that a former Ledger employee was duped. Tether, the stablecoin issuer, has reportedly suspended the hacker’s wallet and the code has been removed.
FINAL TIMELINE AND UPDATE TO CUSTOMERS:
— Ledger (@Ledger) December 14, 2023
4:49pm CET:
Ledger Connect Kit genuine version 1.1.8 is being propagated now automatically. We recommend waiting 24 hours until using the Ledger Connect Kit again.
The investigation continues, here is the timeline of what we know about…